NF-kB p65 (RELA) Sheep Polyclonal Antibody
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Applications | ELISA, EMSA, IP, WB |
| Recommended Dilution | ELISA: 1:2,000. Western Blot: 1:200 - 1:1000. Immunoprecipitation. Gel Super Shift Assays. |
| Reactivities | Human |
| Host | Sheep |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Immunogen | Human p65 (residues 12-317) expressed in E. coli |
| Specificity | This antibody recognizes full length p65 (NF-kB), and proteolytic fragments containing the DNA binding domain. This Sheep anti Human NFkB p65 antibody will also detect proteolytic fragments of NFkB p65 containing the DNA binding RHD domain located in the amino-terminal region. Multiple isoforms of NFkB p65 are generated by alternative splicing. This antibody binds to isoforms 1 and 2 containing the intact RHD domain, but it is unclear whether it will bind to isoforms 3 and 4 which have partial differing deletions within the RHD domain. |
| Formulation | PBS State: Aff - Purified State: Liquid purified IgG farction Stabilizer: 0.5% BSA Preservative: 0.09% Sodium Azide |
| Concentration | lot specific |
| Purification | Affinity chromatography |
| Storage | Store undiluted at 2-8°C for one month or (in aliquots) at -20°C for longer. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Stability | Shelf life: one year from despatch. |
| Database Link | |
| Background | NFkB (Nuclear Factor NF-kappa-B) is a pleiotropic transcription factor that plays a role in many biological processes, including inflammation, immunity, differentiation, cell growth, tumorigenesis, and apoptosis. It is found as a homo- or heterodimeric complex containing the Rel-like domain containing proteins NFkB p65 (RELA/p65), RELB, NFkB1/p105, NFkB1/p50, REL and NFkB2/p52. The heterodimeric NFkB p65/p50 complex is the most abundant one. The dimers bind to kappa-B sites at their target genes, with the affinity of the interaction dependent on the subunit composition of the dimer. Furthermore, different dimers act as transcriptional activators or repressors, with the NFkB p65/p50 and p65-c-Rel complexes acting as activators. NFkB activity is controlled by several different mechanisms, including post-translational modifications, subcellular localisation and interactions with other coactivators or corepressors. NFkB complexes are held in the cytoplasm in an inactive state by interaction with members of the NFkB inhibitor (IkB) family. Typically, phosphorylation of IkB by IkB kinases (IKKs) in response to different activators leads to degradation of the inhibitor, allowing NFkB to translocate into the nucleus. The inhibitory effect of IkBs is primarily exerted through their interaction with NfKB p65. NFkB p65 is ubiquitinated leading to its proteosomal degradation, which is required for termination of the NFkB response. Phosphorylation of NFkB p65 on S536 stimulates acetylation of K310 by CBP, enhancing transcriptional activity. NFkB p65 is also acetylated at K122, enhancing DNA binding and impairing the interaction with NFKBIA. The protein is deacetylated by HDAC3. Invasion of a host by a pathogen is frequently associated with the activation of NF-kB, which coordinates various aspects of immune function required for resistance to infection. |
| Synonyms | NF kappa B p65, NFkB p65, Transcription factor p65, Rel A, NFKB3 |
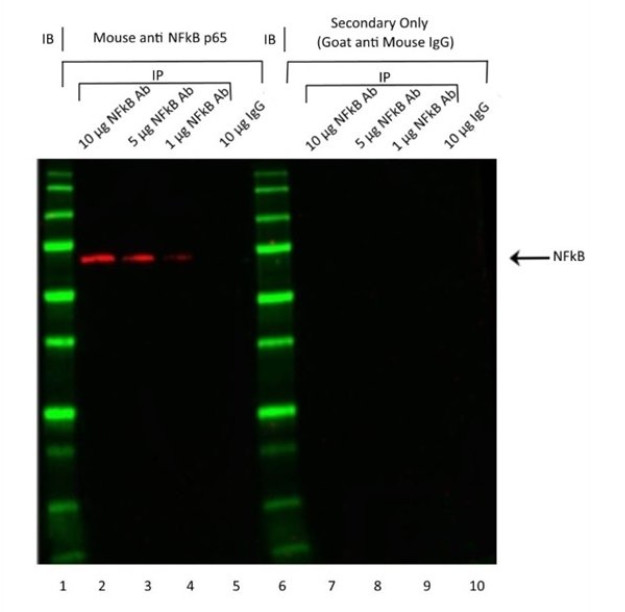
| Reference Data | |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China