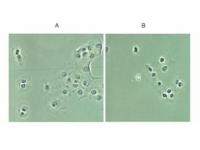
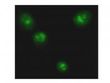
NF-kB p65 (RELA) Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Other products for "RELA"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Applications | IF, IHC |
| Recommended Dilution | ELISA: 1:5,000 - 1:25,000, WB: 1:2,000, IHC: 1:200, IF: 1:200, Gel Shift: 0.5 uL - 1.0 uL |
| Reactivities | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Immunogen | This antibody was purified from whole rabbit serum prepared by repeated immunizations with the NFkB p65 peptide corresponding to the NLS of the human protein conjugated to KLH using maleimide. A residue of cysteine was added to the amino terminal end to facilitate coupling. |
| Formulation | 0.02 M Potassium Phosphate, 0.15 M Sodium Chloride, pH 7.2 |
| Concentration | lot specific |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Storage | Store at -20°C as received. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from date of receipt. |
| Gene Name | RELA proto-oncogene, NF-kB subunit |
| Database Link | |
| Synonyms | NFKB3; p65 |
| Note | NFkB was originally identified as a factor that binds to the immunoglobulin kappa light chain enhancer in B cells. It was subsequently found in non-B cells in an inactive cytoplasmic form consisting of NFkB bound to IkB. NFkB was originally identified as a heterodimeric DNA binding protein complex consisting of p65 (RelA) and p50 (NFKB1) subunits. Other identified subunits include p52 (NFKB2), c-Rel, and RelB. The p65, cRel, and RelB subunits are responsible for transactivation. The p50 and p52 subunits possess DNA binding activity but limited ability to transactivate. p52 has been reported to form transcriptionally active heterodimers with the NFkB subunit p65, similar to p50/p65 heterodimers. Low levels of p52 and p50 homodimers can also exist in cells. The heterodimers of p52/p65 and p50/p65 are regulated by physical inactivation in the cytoplasm by IkB-a. IkB-a binds to the p65 subunit, preventing nuclear localization and DNA binding. IkB-a binding masks the NFkB nuclear localisation signal (NLS). A broad range of external stimuli lead to activation of NFkB and set off signalling cascades that ultimately converge on the IkB kinase (IKK) complex. Activated IKK specifically and directly phosphorylates IkB-a and this phophorylation event targets IkB-a for degradation. As a consequence, NFkB NLS is uncovered and nuclear translocation occurs. |
| Reference Data | |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome, Transcription Factors |
| Protein Pathways | Acute myeloid leukemia, Adipocytokine signaling pathway, Apoptosis, B cell receptor signaling pathway, Chemokine signaling pathway, Chronic myeloid leukemia, Cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway, Epithelial cell signaling in Helicobacter pylori infection, MAPK signaling pathway, Neurotrophin signaling pathway, NOD-like receptor signaling pathway, Pancreatic cancer, Pathways in cancer, Prostate cancer, RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway, Small cell lung cancer, T cell receptor signaling pathway, Toll-like receptor signaling pathway |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China