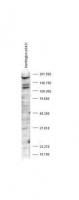
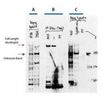
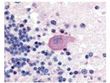
Huntingtin (HTT) Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Other products for "HTT"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Applications | IHC, WB |
| Recommended Dilution | ELISA: 1:10,000 - 1:40,000, WB: 1:500 - 1:3,000, IHC: 1:50 - 1:100 |
| Reactivities | Human |
| Modifications | Phospho-specific |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Immunogen | Huntingtin pS421 Antibody was prepared from whole rabbit serum produced by repeated immunizations with a synthetic peptide corresponding aa 416-424 of Human huntingtin protein. |
| Formulation | 0.02 M Potassium Phosphate, 0.15 M Sodium Chloride, pH 7.2 |
| Concentration | lot specific |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Storage | Store at -20°C as received. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from date of receipt. |
| Gene Name | huntingtin |
| Database Link | |
| Synonyms | HD; IT15 |
| Note | Huntingtin (also known as Huntington's disease protein, Htt and HD protein) is the protein product of a disease gene linked to Huntington's disease, a neuro-degenerative disorder characterized by loss of striatal neurons. This may be caused by an expanded, unstable trinucleotide repeat in the huntingtin gene, which translates as a polyglutamine repeat in the protein product (see partial protein sequence below). The huntingtin gene locus is large, spanning 180 kb and consisting of 67 exons. It is expressed as 2 alternatively polyadenylated forms displaying different relative abundance in various fetal and adult tissues. The genetic defect leading to Huntington's disease may not necessarily eliminate transcription, but may confer a new property on the mRNA or alter the function of the protein. One candidate is the huntingtin-associated protein-1, highly expressed in brain, which has increased affinity for huntingtin protein with expanded polyglutamine repeats. Normal huntingtin protein shows a cytoplasmic localization. This protein is widely expressed with the highest level of expression in the brain (nerve fibers, varicosities, and nerve endings). In the brain, the regions where it can be mainly found are the cerebellar cortex, the neocortex, the striatum, and the hippocampal formation. |
| Reference Data | |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome |
| Protein Pathways | Huntington's disease |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China