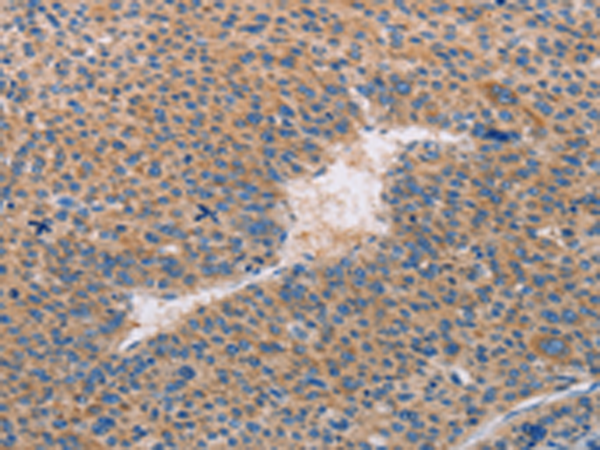
Caspase 10 (CASP10) Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Other products for "CASP10"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Applications | IHC |
| Recommended Dilution | IHC: 25-100 Positive control: Human liver cancer Predicted cell location: Cytoplasm |
| Reactivities | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein corresponding to a region derived from 228-522 amino acids of human caspase 10, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase |
| Formulation | PBS pH7.3, 0.05% NaN3, 50% glycerol |
| Concentration | lot specific |
| Purification | Antigen affinity purification |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Storage | Store at -20°C as received. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from date of receipt. |
| Gene Name | caspase 10 |
| Database Link | |
| Background | This gene encodes a protein which is a member of the cysteine-aspartic acid protease (caspase) family. Sequential activation of caspases plays a central role in the execution-phase of cell apoptosis. Caspases exist as inactive proenzymes which undergo proteolytic processing at conserved aspartic residues to produce two subunits, large and small, that dimerize to form the active enzyme. This protein cleaves and activates caspases 3 and 7, and the protein itself is processed by caspase 8. Mutations in this gene are associated with type IIA autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome, non-Hodgkin lymphoma and gastric cancer. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described for this gene. |
| Synonyms | ALPS2; FLICE2; MCH4 |
| Reference Data | |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome, Protease |
| Protein Pathways | Apoptosis, RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China