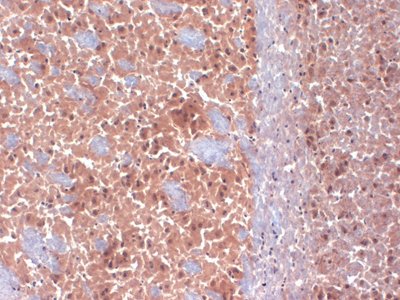
Cacna1d Mouse Monoclonal Antibody [Clone ID: S38-8]
Other products for "Cacna1d"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Clone Name | S38-8 |
| Applications | IF, IHC |
| Recommended Dilution | WB: 1-10ug/ml, IHC: 0.1-1.0ug/ml, IF: 1.0-10ug/ml |
| Reactivities | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Mouse |
| Isotype | IgG1 |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein amino acids 2025-2161 of rat Cav1.3 |
| Formulation | PBS pH7.4, 50% glycerol |
| Concentration | lot specific |
| Purification | Protein G Purified |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Storage | Store at -20°C as received. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from date of receipt. |
| Gene Name | calcium voltage-gated channel subunit alpha1 D |
| Database Link | |
| Background | Ion channels are integral membrane proteins that help establish and control the small voltage gradient across the plasma membrane of living cells by allowing the flow of ions down their electrochemical gradient . They are present in the membranes that surround all biological cells because their main function is to regulate the flow of ions across this membrane. Whereas some ion channels permit the passage of ions based on charge, others conduct based on a ionic species, such as sodium or potassium. Furthermore, in some ion channels, the passage is governed by a gate which is controlled by chemical or electrical signals, temperature, or mechanical forces.There are a few main classifications of gated ion channels. There are voltage- gated ion channels, ligand-gated, other gating systems and finally those that are classified differently, having more exotic characteristics. The first are voltage- gated ion channels which open and close in response to membrane potential. These are then separated into sodium, calcium, potassium, proton, transient receptor, and cyclic nucleotide-gated channels; each of which is responsible for a unique role. Ligand-gated ion channels are also known as ionotropic receptors, and they open in response to specific ligand molecules binding to the extracellular domain of the receptor protein. The other gated classifications include activation and inactivation by second messengers, inward-rectifier potassium channels, calcium-activated potassium channels, two-pore-domain potassium channels, light-gated channels, mechano-sensitive ion channels and cyclic nucleotide-gated channels. Finally, the other classifications are based on less normal characteristics such as two-pore channels, and transient receptor potential channels .Specifically, CaV1.3, also known as the calcium channel, voltage-dependent, L type, alpha 1D subunit (CACNA1D), is a human gene. CaV1.3 subunits are primarily expressed in neurons and neuroendocine cells. Some studies suggest however that CaV1.3 is also found in the atria, and may figure prominently in atrial arrhythmias . CaV1.3 also carries the primary sensory receptors of the mammalian cochlea, and are also expressed in the electromotile outer hair cells . |
| Synonyms | CACH3; CACN4; CACNL1A2; Cav1.3; CCHL1A2 |
| Note | Detects ~250kDa. No cross-reactivity against Cav1.2 |
| Reference Data | |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China