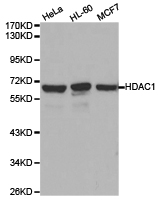
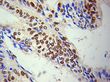
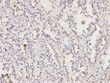
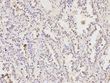
HDAC1 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Frequently bought together (3)
Transient overexpression lysate of histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1)
USD 396.00
Other products for "HDAC1"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Applications | ICC/IF, IHC, IP, WB |
| Recommended Dilution | WB 1:500 - 1:2000;IHC 1:50 - 1:200;IF 1:50 - 1:200;IP 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivities | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Immunogen | N term -peptide of human HDAC1 |
| Formulation | Store at -20C or -80C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3 |
| Concentration | lot specific |
| Purification | Affinity purification |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Storage | Store at -20°C as received. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from date of receipt. |
| Gene Name | histone deacetylase 1 |
| Database Link | |
| Background | Acetylation of the histone tail causes chromatin to adopt an "open" conformation, allowing increased accessibility of transcription factors to DNA. The identification of histone acetyltransferases (HATs) and their large multiprotein complexes has yielded important insights into how these enzymes regulate transcription. HAT complexes interact with sequence-specific activator proteins to target specific genes. In addition to histones, HATs can acetylate nonhistone proteins, suggesting multiple roles for these enzymes. In contrast, histone deacetylation promotes a "closed" chromatin conformation and typically leads to repression of gene activity. Mammalian histone deacetylases can be divided into three classes on the basis of their similarity to various yeast deacetylases. Class I proteins (HDACs 1, 2, 3, and 8) are related to the yeast Rpd3-like proteins, those in class II (HDACs 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, and 10) are related to yeast Hda1-like proteins, and class III proteins are related to the yeast protein Sir2. Inhibitors of HDAC activity are now being explored as potential therapeutic cancer agents. |
| Synonyms | GON-10; HD1; RPD3; RPD3L1 |
| Reference Data | |
| Protein Families | Adult stem cells, Druggable Genome, Stem cell - Pluripotency, Stem cell relevant signaling - DSL/Notch pathway, Transcription Factors |
| Protein Pathways | Cell cycle, Chronic myeloid leukemia, Huntington's disease, Notch signaling pathway, Pathways in cancer |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China