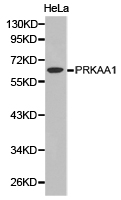
AMPK alpha 1 (PRKAA1) Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Frequently bought together (2)
Transient overexpression lysate of protein kinase, AMP-activated, alpha 1 catalytic subunit (PRKAA1), transcript variant 1
USD 605.00
Other products for "PRKAA1"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Applications | ICC/IF, WB |
| Recommended Dilution | WB 1:500 - 1:2000;IF 1:50- 1:200 |
| Reactivities | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Immunogen | Recombinant protein of human PRKAA1 |
| Formulation | Store at -20C or -80C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3 |
| Concentration | lot specific |
| Purification | Affinity purification |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Storage | Store at -20°C as received. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from date of receipt. |
| Gene Name | protein kinase AMP-activated catalytic subunit alpha 1 |
| Database Link | |
| Background | AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is highly conserved from yeast to plants and animals and plays a key role in the regulation of energy homeostasis. AMPK is a heterotrimeric complex composed of a catalytic a subunit and regulatory β and ? subunits, each of which is encoded by two or three distinct genes (a1, 2; β1, 2; ?1, 2, 3). The kinase is activated by an elevated AMP/ATP ratio due to cellular and environmental stress, such as heat shock, hypoxia, and ischemia. The tumor suppressor LKB1, in association with accessory proteins STRAD and MO25, phosphorylates AMPKa at Thr172 in the activation loop, and this phosphorylation is required for AMPK activation. AMPKa is also phosphorylated at Thr258 and Ser485 (for a1; Ser491 for a2). The upstream kinase and the biological significance of these phosphorylation events have yet to be elucidated. The β1 subunit is post-translationally modified by myristoylation and multi-site phosphorylation including Ser24/25, Ser96, Ser101, Ser108, and Ser182. Phosphorylation at Ser108 of the β1 subunit seems to be required for the activation of AMPK enzyme, while phosphorylation at Ser24/25 and Ser182 affects AMPK localization. Several mutations in AMPK? subunits have been identified, most of which are located in the putative AMP/ATP binding sites (CBS or Bateman domains). Mutations at these sites lead to reduction of AMPK activity and cause glycogen accumulation in heart or skeletal muscle. Accumulating evidence indicates that AMPK not only regulates the metabolism of fatty acids and glycogen, but also modulates protein synthesis and cell growth through EF2 and TSC2/mTOR pathways, as well as blood flow via eNOS/nNOS. |
| Synonyms | AMPK; AMPKa1 |
| Reference Data | |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome, Protein Kinase |
| Protein Pathways | Adipocytokine signaling pathway, Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), Insulin signaling pathway, mTOR signaling pathway, Regulation of autophagy |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China