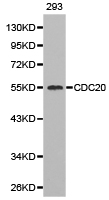
CDC20 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Frequently bought together (3)
Recombinant protein of human cell division cycle 20 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (CDC20)
USD 823.00
Transient overexpression lysate of cell division cycle 20 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (CDC20)
USD 396.00
Other products for "CDC20"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Applications | ICC/IF, WB |
| Recommended Dilution | WB 1:500 - 1:2000;IF 1:50- 1:200 |
| Reactivities | Human, Mouse |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Immunogen | Recombinant protein of human CDC20 |
| Formulation | Store at -20C or -80C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3 |
| Concentration | lot specific |
| Purification | Affinity purification |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Storage | Store at -20°C as received. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from date of receipt. |
| Gene Name | cell division cycle 20 |
| Database Link | |
| Background | The cell division cycle demands accuracy to avoid the accumulation of genetic damage. This process is controlled by molecular circuits called "checkpoints" that are common to all eukaryotic cells. Checkpoints monitor DNA integrity and cell growth prior to replication and division at the G1/S and G2/M transitions, respectively. The cdc2-cyclin B kinase is pivotal in regulating the G2/M transition. Cdc2 is phosphorylated at Thr14 and Tyr15 during G2-phase by the kinases Wee1 and Myt1, rendering it inactive. The tumor suppressor protein retinoblastoma (Rb) controls progression through the late G1 restriction point (R) and is a major regulator of the G1/S transition. During early and mid G1-phase, Rb binds to and represses the transcription factor E2F. The phosphorylation of Rb late in G1-phase by CDKs induces Rb to dissociate from E2F, permitting the transcription of S-phase-promoting genes. In vitro, Rb can be phosphorylated at multiple sites by cdc2, cdk2, and cdk4/6. DNA damage triggers both the G2/M and the G1/S checkpoints. DNA damage activates the DNA-PK/ATM/ATR kinases, which phosphorylate Chk at Ser345, Chk2 at Thr68 and p53. The Chk kinases inactivate cdc25 via phosphorylation at Ser216, blocking the activation of cdc2.CDC20 binds to and activates the anaphase-promoting complex (APC) during mitosis and G1 phase of the cell cycle. Moreover, CDC20 is necessary for ubiquitin ligase activity of the APC/cyclosome (APC/C). In metaphase MAD2L1 inactivates the CDC20-APC/C complex, while in anaphase this inhibition is lost and CDC20-APC/C degrades its substrates. p53 and p21 suppress expression of CDC20 upon genotoxic stresses and ectopic introduction of p53. siRNA mediated knock-down of CDC20 in cancer cells leads to attenuated cell growth and induces G(2)/M arrest, suggesting that CDC20 is a possible therapeutic target of cancer. Organization of neuronal circuits requires presynaptic axonal differentiatio. |
| Synonyms | bA276H19.3; CDC20A; p55CDC |
| Reference Data | |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome |
| Protein Pathways | Cell cycle, Oocyte meiosis, Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China