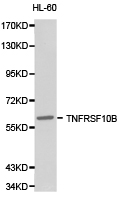
DR5 (TNFRSF10B) Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Frequently bought together (2)
Transient overexpression lysate of tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 10b (TNFRSF10B), transcript variant 1
USD 436.00
Other products for "DR5"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Applications | ELISA, WB |
| Recommended Dilution | WB,1:500 - 1:2000 ELISA,Recommended starting concentration is 1 μg/mL. Please optimize the concentration based on your specific assay requirements. |
| Reactivities | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Formulation | Buffer: PBS with 0.09% Sodium azide,50% glycerol,pH7.3. |
| Concentration | lot specific |
| Purification | Affinity purification |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Storage | Store at -20℃. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from date of receipt. |
| Predicted Protein Size | 48kDa |
| Gene Name | tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 10b |
| Database Link | |
| Background | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the TNF-receptor superfamily, and contains an intracellular death domain. This receptor can be activated by tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TNFSF10/TRAIL/APO-2L), and transduces an apoptosis signal. Studies with FADD-deficient mice suggested that FADD, a death domain containing adaptor protein, is required for the apoptosis mediated by this protein. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms and one non-coding transcript have been found for this gene. |
| Synonyms | CD262; DR5; KILLER; TRAIL-R2; TRAILR2; TRICK2; TRICK2A; TRICK2B; TRICKB; ZTNFR9 |
| Reference Data | |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome, Transmembrane |
| Protein Pathways | Apoptosis, Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction, Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity, p53 signaling pathway |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China