KCNE3 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Other products for "KCNE3"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
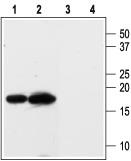
| Applications | WB |
| Recommended Dilution | WB: 1:200-1:2000; IHC: 1:100-1:3000 |
| Reactivities | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Immunogen | Peptide (C)RSRKVDKRSDPYH, corresponding to amino acid residues 81-93 of human KCNE3 (Accession Q9Y6H6 ). Intracellular, C-terminal part. |
| Formulation | Lyophilized. Concentration before lyophilization ~0.8mg/ml (lot dependent, please refer to CoA along with shipment for actual concentration). Buffer before lyophilization: Phosphate buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.4, 1 % BSA, 0.025% NaN3. |
| Purification | Affinity purified on immobilized antigen. |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Storage | Store at -20°C as received. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from date of receipt. |
| Gene Name | potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily E regulatory subunit 3 |
| Database Link | |
| Background | KCNE3 (or MiRP2) is a member of a family of proteins that regulate the activity of voltage-dependent K+ channels. The other members of the family are KCNE1 (IsK, MiNK), KCNE2 (MiRP1), KCNE4 (MiRP3) and KCNE5 (MiRP4). KCNE1 is the founding member of the family and was initially believed to form a K+ channel itself, but was latter recognized that it worked as a regulatory b subunit associated with the Kv7.1 (KCNQ1) a protein. KCNE3 was discovered based on its homology with KCNE1. The KCNE regulatory subunits are small proteins (14- 20 kD) with a type-1 integral membrane topology. It is believed that both the cytoplasmic C-terminus tail and the transmembrane domain are necessary for the interaction with the a subunits. The stoichiometry of the KCNE subunits with their partner a subunits in the native channels is not clear and ratios ranging from 2 to 14 KCNE subunits per 4 a subunits have been proposed. KCNE3 is relatively widely expressed in several tissues with prominent expression in the kidney and skeletal muscle. KCNE3 is quite promiscuous and associations with Kv7.1, Kv3.4, Kv7.4 (KCNQ4), Kv11.1 (HERG), Kv2.1 and Kv3.1b have been demonstrated. The best characterized interactions are with the former two proteins. KCNE3 interacts with Kv7.1 in epithelial cells of the gastrointestinal tract where it appears to be important for Na+ absorption. In skeletal muscle KCNE3 couples to Kv3.4 to regulate muscle function. Indeed, a mutation in KCNE3 (R83H) has been associated with an inherited form of periodic paralysis (Thyrotoxic hypokalemic periodic paralysis). |
| Synonyms | HOKPP; HYPP; MiRP2 |
| Reference Data | |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome, Ion Channels: Other, Transmembrane |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China