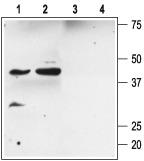
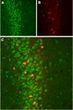
KCNMB2 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Other products for "KCNMB2"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Applications | IHC, WB |
| Recommended Dilution | WB: 1:200-1:2000; IHC: 1:100-1:3000 |
| Reactivities | Human, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Immunogen | Peptide (C)RHDEKRNIYQKIRDHDLLD, corresponding to amino acid residues 14-32 of human sloÃ?2.Intracellular, N-terminal part. |
| Formulation | Lyophilized. Concentration before lyophilization ~0.8mg/ml (lot dependent, please refer to CoA along with shipment for actual concentration). Buffer before lyophilization: phosphate buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.4, 1% BSA, 0.05% NaN3. |
| Purification | Affinity purified on immobilized antigen. |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Storage | Store at -20°C as received. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from date of receipt. |
| Gene Name | potassium calcium-activated channel subfamily M regulatory beta subunit 2 |
| Database Link | |
| Background | sloÃ?2 is a member the regulatory Ã? subunit family that controls the activity of the large conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel KCa1.1. This family includes four members with a shared topology: two trans-membrane domains, short intracellular N- and C-termini and a large extracellular region and a distinct tissue distribution. sloÃ?2 expression is relatively broad and includes expression in brain, heart, kidney adrenal chromaffin cells and ovary. The KCa1.1 K+ channel can be activated by either an increase in intracellular Ca2+ concentration or by membrane depolarization. The regulatory Ã? subunits increase the sensitivity of the pore-forming KCa1.1 subunit to Ca2+ and membrane voltage and they may also change the channel pharmacology. The sloβ2 subunit is unique in that it is able to induce a rapid and complete inactivation of the KCa1.1 channel in a manner that closely resembles the ball-and-chain inactivation of the voltage-dependent K+ (Kv) channels. In other words, the inactivation is dependent on a sequence in the N-terminal part of the sloÃ?2 subunit that appears to block the mouth of the ion permeation pathway. The physiological significance of the sloÃ?2 subunit is not clear, but it appears to participate in the inactivation of the KCa1.1 channel in hippocampal CA1 neurons and adrenal chromaffin cells. |
| Synonyms | MGC22431 |
| Reference Data | |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome, Ion Channels: Other, Transmembrane |
| Protein Pathways | Vascular smooth muscle contraction |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China