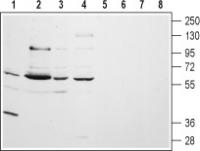
Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor M5 (CHRM5) Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Other products for "CHRM5"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Applications | WB |
| Recommended Dilution | WB: 1:200-1:2000 |
| Reactivities | Human, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Immunogen | Peptide (C)HNATTVNGTPVNHQPLER, corresponding to amino acid residues 7-24 of human M5 muscarinic receptor. Extracellular, N-terminus. |
| Formulation | Lyophilized. Concentration before lyophilization ~0.8mg/ml (lot dependent, please refer to CoA along with shipment for actual concentration). Buffer before lyophilization: Phosphate buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.4, 1% BSA, 0.05% NaN3. |
| Purification | Affinity purified on immobilized antigen. |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Storage | Store at -20°C as received. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from date of receipt. |
| Gene Name | cholinergic receptor muscarinic 5 |
| Database Link | |
| Background | Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter which activates two different groups of receptors: nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) which belong to the superfamily of ligand-gated ion channels and muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChR), belonging to the G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) superfamily. There are five separate gene products that put together this GPCR subfamily, M1-M5, and like all GPCR have seven transmembrane spanning domains. Generally, M1, M3 and M5 muscarinic receptors are known to activate phospholipase C (PLC) via Gq coupling, while M2 and M4 muscarinic receptors couple to Gi/o, and therefore inhibit adenylate cyclase. This classification is however not clear cut. mAChR can activate adenylate cyclase by coupling to Gs. In addition, M2 and M4 muscarinic receptors, when overexpressed can also activate adenylate cyclase in some systems. Evidence suggests that muscarinic receptors can form homo or heterodimers at that the dimer formed can subsequently affect the downstream signaling pathways. Muscarinic receptors have been shown to regulate voltage-gated Ca2+ channels, namely Cav2.1 as well acid sensing ion channels (ASIC). Generally speaking the actions of muscarinic receptors on ion channels can be either via 2nd messengers or through their direct action on the channels once activated. Furthermore, muscarinic receptors can also promote endocytosis of ion channels (Kv1.2 for example) by recruiting tyrosine kinases that phosphorylate the channel in order to terminate its activity. Other diverse and important functions of muscarinic receptors include cell growth, survival and physiology. Expression of muscarinic receptors is found in neurons in the central nervous system as well as in the peripheral nervous system. In the non-nervous system, these receptors are expressed in the cardiac and smooth muscle, lung, intestine, ovary and urothelium. M5 muscarinic receptor has been the hardest receptor to study as there is no specific pharmacology targeted against the receptor and no high level of expression has been detected in tissues. However, the effects of single knockout mice were studied and it was observed that in M5 muscarinic receptor knockout mice, there is a moderate decrease in ligand binding in the lung and bladder, two organs expressing M5 muscarinic receptor. In addition, it has been proposed that M5 muscarinic receptor may be involved in interstitial cystitis, a urinary bladder disorder. |
| Synonyms | HM5 |
| Reference Data | |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome, GPCR, Transmembrane |
| Protein Pathways | Calcium signaling pathway, Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction, Regulation of actin cytoskeleton |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China