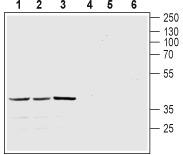
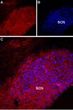
Mtnr1a Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Other products for "Mtnr1a"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Applications | IHC, WB |
| Recommended Dilution | WB: 1:200-1:2000; IHC: 1:100-1:3000 |
| Reactivities | Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Immunogen | Peptide (C)RVKPDNKPKLKPQD, corresponding to amino acid residues 223-236 of mouse Melatonin Receptor Type 1 . 3rd intracellular loop. |
| Formulation | Lyophilized. Concentration before lyophilization ~0.8mg/ml (lot dependent, please refer to CoA along with shipment for actual concentration). Buffer before lyophilization: Phosphate buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.4, 1% BSA, 0.05% NaN3. |
| Purification | Affinity purified on immobilized antigen. |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Storage | Store at -20°C as received. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from date of receipt. |
| Gene Name | melatonin receptor 1A |
| Database Link | |
| Background | Melatonin (N-acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine) is a product of tryptophan metabolism. It is synthesized in the pineal gland and is secreted to control the circadian rhythm. Melatonin is also synthesized in the gastrointestinal tract, retina, skin and other tissues where it acts in a autocrine or paracrine manner. The role of melatonin in these tissues is independent of its role in the circadian rhythm, where it plays a role in energy metabolism, physiological growth, differentiation and responsiveness in stress stimuli. The pleiotropic effects of melatonin have given rise to various therapeutic possibilities for this molecule. For example; anti-stress, sexual dysfunction, obesity, gallbladder stones. To date, the only therapeutic uses for melatonin remain to treat sleep disorders, depression, migraine and headaches. Melatonin exerts its effects through two G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs); melatonin receptor type 1 and melatonin receptor type 2 (MT1 and MT2). Like all GPCRs, they have seven transmembrane domains and extracellular N-terminal and cytoplasmic C-terminal tails. The binding of melatonin to either receptor activates Gi, thereby activating PLC, thus increasing intracellular Ca2+ levels. Both receptors structurally bind melatonin in the same manner, although MT2 displays a much higher affinity for the hormone. Just like melatonin levels are detected in many tissues, the expression patterns of the two receptors are also quite broad. For example, MT1 is detected in the brain, retina and kidneys and MT2 is expressed in brain and in the retina. MT1 is involved in sleep regulation and might also have effects on peripheral vasoconstriction. MT2 may play an important physiological role in the retina and might regulate body temperature. |
| Synonyms | MEL-1A-R; MT1 |
| Reference Data | |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China