Kcnj1 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Other products for "Kcnj1"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Applications | IHC, WB |
| Recommended Dilution | WB: 1:200-1:2000; IHC: 1:100-1:3000 |
| Reactivities | Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
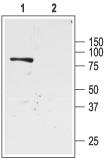
| Immunogen | GST fusion protein with sequence HNFGKTVEVETPHCAMCLYNEKDARARMKRGYDNPNFVLSEVDET DDTQM, corresponding to amino acids 342-391 of rat ROMK1, (MW: 33 kDa). Intracellular, C-terminus. |
| Formulation | Lyophilized. Concentration before lyophilization ~0.8mg/ml (lot dependent, please refer to CoA along with shipment for actual concentration). Buffer before lyophilization: Phosphate buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.4, 1% BSA, 0.025% NaN3. |
| Purification | The serum was depleted of anti-GST antibodies by affinity chromatography on immobilized GST, and then the antibody was affinity purified on immobilized Kir1.1-GST. |
| Storage | Store at -20°C as received. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from date of receipt. |
| Gene Name | potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily J member 1 |
| Database Link | |
| Background | Kir1.1 (ROMK1) was the first member of the family of inward rectifying K+ channels to be cloned. The family includes 15 members that are structurally and functionally different from the voltage-dependent K+ channels.The familyâ??s topology consists of two transmembrane domains that flank a single and highly conserved pore region with intracellular N- and C-termini. As is the case for the voltage-dependent K+ channels the functional unit for the Kir channels is composed of four subunits that can assembly as either homo or heterotetramers.Kir channels are characterized by a K+ efflux that is limited by depolarizing membrane potentials thus making them essential for controlling resting membrane potential and K+ homeostasis.As its original name indicates (ROMK1 stands for Renal Outer Medullary K+ channel) Kir1.1 is strongly expressed in the kidney in the apical membrane of several kidney segments such as the thick ascending loop of Henle (TAL) and the cortical collecting duct (CCD). In addition, the channel is also expressed in the brain mainly in the cortex and hippocampus.Kir1.1 plays a key role in K+ recycling in the loop of Henle. Indeed, loss of function mutations in the Kir1.1 gene cause Bartterâ??s syndrome type II, a recessive autosomal disease characterized by the impairment of K+ efflux and the subsequent inability of the NKCC2 transporter to continue NaCl uptake. This leads to a high salt concentration in the urine that induces osmotic diuresis and low plasma volume.Pharmacologically, the Kir1.1 channel can be inhibited by several general K+ channel blockers such as Tertiapin (#STT-250), however the scorpion toxin Lq2 (#RTL-550) specifically and potently inhibits Kir1.1 channels. |
| Synonyms | Kir1.1; OTTHUMP00000045938; ROMK; ROMK1 |
| Reference Data | |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China