Kcnj10 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Other products for "Kcnj10"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Applications | WB |
| Recommended Dilution | WB: 1:200-1:2000; IHC: 1:100-1:3000 |
| Reactivities | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Immunogen | Peptide (C)KLEE SLREQ AEKEG SALSV R, corresponding to amiono acid residues 356-375 of rat Kir4.1. Intracellular, C-terminus. |
| Formulation | Lyophilized. Concentration before lyophilization ~0.8mg/ml (lot dependent, please refer to CoA along with shipment for actual concentration). Buffer before lyophilization: phosphate buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.4, 1% BSA, 0.05% NaN3. |
| Purification | Affinity purified on immobilized antigen. |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Storage | Store at -20°C as received. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from date of receipt. |
| Gene Name | potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily J member 10 |
| Database Link | |
| Background | Kir4.1 is a member of the inward rectifying K+ channel family. The family includes 15 members that are structurally and functionally different from the voltage-dependent K+ channels.The familyâ??s topology consists of two transmembrane domains that flank a single and highly conserved pore region with intracellular N- and C-termini. As is the case for the voltage-dependent K+ channels the functional unit for the Kir channels is composed of four subunit that can assembly as either homo or heteromers.Kir channels are characterized by a K+ efflux that is limited by depolarizing membrane potentials thus making them essential for controlling resting membrane potential and K+ homeostasis.Kir4.1 is a member of the Kir4 subfamily that includes one other member: Kir4.2. Kir4.1 can co-assemble with Kir4.2 but also with other Kir channels such as Kir2.1 and Kir5.1.The Kir4 subfamily has been classified as weak rectifiers with intermediate conductance. Kir4.1 is mainly expressed in brain, specifically in glia cells, but also in retina, ear and kidney.It has been proposed that Kir4.1 has an essential role in glial K+ buffering, a process that re-uptakes the K+released during neuronal activity into the intracellular interstitial space. Loss of Kir4.1 causes retinal defects and loss of endochoclear potential. |
| Synonyms | BIRK-10; KCNJ13-PEN; Kir1.2; Kir4.1; SESAME |
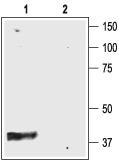
| Reference Data | |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China