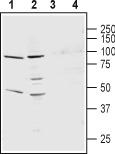
Kcns1 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Other products for "Kcns1"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Applications | IHC, WB |
| Recommended Dilution | WB: 1:200-1:2000; IHC: 1:100-1:3000 |
| Reactivities | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Immunogen | Peptide (C)EFQNEDGEVDDPVLE, corresponding to amino acid residues 209-223 of rat Kv9.3 . 1st extracellular loop. |
| Formulation | Lyophilized. Concentration before lyophilization ~0.8mg/ml (lot dependent, please refer to CoA along with shipment for actual concentration). Buffer before lyophilization: phosphate buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.4, 1% BSA, 0.05% NaN3. |
| Purification | Affinity purified on immobilized antigen. |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Storage | Store at -20°C as received. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from date of receipt. |
| Gene Name | potassium voltage-gated channel, modifier subfamily S, member 1 |
| Database Link | |
| Background | K+ channels are transmembrane proteins expressed in many excitable and non-excitable cells. Functional entities are formed by the tetrameric assembly of a subunits which could be done in a homomeric or heteromeric fashion. In addition, the association of b subunits is also required for the proper function of K+ channels. Various splice variants are also expressed, thereby complicating the picture. K+ channels belonging to the K V9 subfamily resemble to the delayed-rectifier class of K+ channel a subunits. These channels include six transmembrane domains, an ion selective pore, a leucine zipper and positively charged amino acids in S4 the voltage sensor domain. Interestingly, both KV9.1 and KV9.3 channels are electrically silent delayed rectifying K+ channels. However, they are responsible for modifying the activity of other K+ channels such as that of KV2.1, yielding currents different from those of KV2.1 on its own. KV9.1 is mainly expressed in the brain, human lens epithelial cells, kidney, prostate and testis. That of KV9.3 is more generalized and ubiquitous.Interestingly, a polymorphism in the gene encoding for KV9.1 was identified and associated with high risks of suffering from neuropathic pain3. Evidently, additional work needs to be done to evaluate and decipher the role of KV9.1 (if at all) in chronic pain states. |
| Synonyms | Kv9.1 |
| Reference Data | |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China