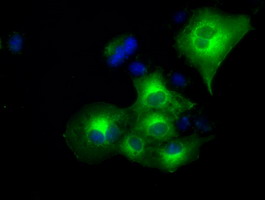
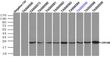
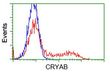
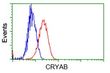
Alpha B Crystallin (CRYAB) Mouse Monoclonal Antibody [Clone ID: OTI1G1]
CAT#: TA500590
CRYAB (Alpha B Crystallin) mouse monoclonal antibody, clone OTI1G1 (formerly 1G1)
Size: 30 ul
Formulation: Carrier Free
View other "OTI1G1" antibodies (2)
Special Offer: Get a 15% discount on this product. Use code: “NEURO15".
USD 823.00
USD 436.00
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Clone Name | OTI1G1 |
| Applications | FC, IF, IP |
| Recommended Dilution | IF 1:100, FLOW 1:100, IP 2ug/500ul |
| Reactivities | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Mouse |
| Isotype | IgG1 |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Immunogen | Full length human recombinant protein of human CRYAB (NP_001876) produced in HEK293T cell. |
| Formulation | PBS (pH 7.3) containing 1% BSA, 50% glycerol and 0.02% sodium azide. |
| Concentration | 1 mg/ml |
| Purification | Purified from mouse ascites fluids or tissue culture supernatant by affinity chromatography (protein A/G) |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Storage | Store at -20°C as received. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from date of receipt. |
| Predicted Protein Size | 20 kDa |
| Gene Name | crystallin alpha B |
| Database Link | |
| Background | Crystallins are separated into two classes: taxon-specific, or enzyme, and ubiquitous. The latter class constitutes the major proteins of vertebrate eye lens and maintains the transparency and refractive index of the lens. Since lens central fiber cells lose their nuclei during development, these crystallins are made and then retained throughout life, making them extremely stable proteins. Mammalian lens crystallins are divided into alpha, beta, and gamma families; beta and gamma crystallins are also considered as a superfamily. Alpha and beta families are further divided into acidic and basic groups. Seven protein regions exist in crystallins: four homologous motifs, a connecting peptide, and N- and C-terminal extensions. Alpha crystallins are composed of two gene products: alpha-A and alpha-B, for acidic and basic, respectively. Alpha crystallins can be induced by heat shock and are members of the small heat shock protein (sHSP also known as the HSP20) family. They act as molecular chaperones although they do not renature proteins and release them in the fashion of a true chaperone; instead they hold them in large soluble aggregates. Post-translational modifications decrease the ability to chaperone. These heterogeneous aggregates consist of 30-40 subunits; the alpha-A and alpha-B subunits have a 3:1 ratio, respectively. Two additional functions of alpha crystallins are an autokinase activity and participation in the intracellular architecture. Alpha-A and alpha-B gene products are differentially expressed; alpha-A is preferentially restricted to the lens and alpha-B is expressed widely in many tissues and organs. Elevated expression of alpha-B crystallin occurs in many neurological diseases; a missense mutation cosegregated in a family with a desmin-related myopathy. [provided by RefSeq] |
| Synonyms | CMD1II; CRYA2; CTPP2; CTRCT16; HEL-S-101; HSPB5; MFM2 |
| Reference Data | |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
| Antibody Resources |
{0} Product Review(s)
Be the first one to submit a review






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China