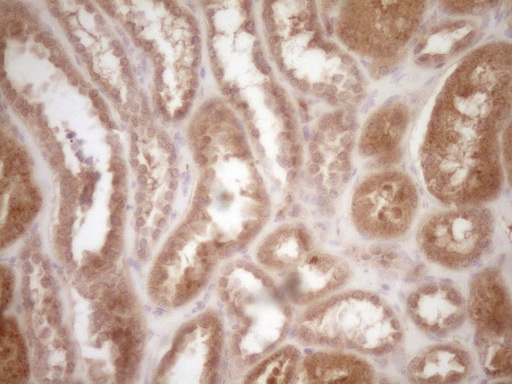
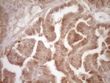
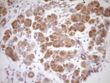
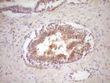
Protein Z (PROZ) Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (Biotin conjugated) [Clone ID: OTI4D5]
CAT#: TA806759AM
PROZ mouse monoclonal antibody, clone OTI4D5 (formerly 4D5), Biotinylated
Other products for "PROZ"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Clone Name | OTI4D5 |
| Applications | IHC |
| Recommended Dilution | IHC 1:150 |
| Reactivities | Human |
| Host | Mouse |
| Isotype | IgG2a |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Immunogen | Human recombinant protein fragment corresponding to amino acids 115-400 of human PROZ(NP_003882) produced in E.coli. |
| Formulation | PBS (PH 7.3) containing 1% BSA, 50% glycerol and 0.02% sodium azide. |
| Concentration | 0.5 mg/ml |
| Purification | Purified from mouse ascites fluids or tissue culture supernatant by affinity chromatography (protein A/G) |
| Conjugation | Biotin |
| Storage | Store at -20°C as received. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from date of receipt. |
| Predicted Protein Size | 40.3 kDa |
| Gene Name | protein Z, vitamin K dependent plasma glycoprotein |
| Database Link | |
| Background | This gene encodes a liver vitamin K-dependent glycoprotein that is synthesized in the liver and secreted into the plasma. The encoded protein plays a role in regulating blood coagulation by complexing with protein Z-dependent protease inhibitor to directly inhibit activated factor X at the phospholipid surface. Deficiencies in this protein are associated with an increased risk of ischemic arterial diseases and fetal loss. Mutations in this gene are the cause of protein Z deficiency. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jan |
| Synonyms | PZ |
| Reference Data | |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome, Protease, Secreted Protein |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China