Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor alpha 7 (CHRNA7) Human Gene Knockout Kit (CRISPR)
CAT#: KN221382LP
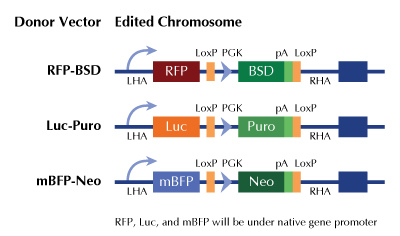
CHRNA7 - human gene knockout kit via CRISPR, HDR mediated
HDR-mediated knockout kit validation
USD 1,290.00
4 Weeks*
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Format | 2 gRNA vectors, 1 GFP-puro donor, 1 scramble control |
| Donor DNA | Luciferase-Puro |
| Symbol | CHRNA7 |
| Locus ID | 1139 |
| Disclaimer | The kit is designed based on the best knowledge of CRISPR technology. The system has been functionally validated for knocking-in the cassette downstream the native promoter. The efficiency of the knock-out varies due to the nature of the biology and the complexity of the experimental process. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NM_000746, NM_001190455, NR_046324, N54079 |
| Synonyms | CHRNA7-2; NACHRA7 |
| Summary | The nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) are members of a superfamily of ligand-gated ion channels that mediate fast signal transmission at synapses. The nAChRs are thought to be hetero-pentamers composed of homologous subunits. The proposed structure for each subunit is a conserved N-terminal extracellular domain followed by three conserved transmembrane domains, a variable cytoplasmic loop, a fourth conserved transmembrane domain, and a short C-terminal extracellular region. The protein encoded by this gene forms a homo-oligomeric channel, displays marked permeability to calcium ions and is a major component of brain nicotinic receptors that are blocked by, and highly sensitive to, alpha-bungarotoxin. Once this receptor binds acetylcholine, it undergoes an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane. This gene is located in a region identified as a major susceptibility locus for juvenile myoclonic epilepsy and a chromosomal location involved in the genetic transmission of schizophrenia. An evolutionarily recent partial duplication event in this region results in a hybrid containing sequence from this gene and a novel FAM7A gene. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2012] |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
Other Versions
| SKU | Description | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| KN221382 | CHRNA7 - human gene knockout kit via CRISPR, HDR mediated |
USD 1,290.00 |
|
| KN221382BN | CHRNA7 - human gene knockout kit via CRISPR, HDR mediated |
USD 1,290.00 |
|
| KN221382RB | CHRNA7 - human gene knockout kit via CRISPR, HDR mediated |
USD 1,290.00 |
|
| KN421382 | CHRNA7 - KN2.0, Human gene knockout kit via CRISPR, non-homology mediated. |
USD 1,290.00 |
|
| GA100816 | CHRNA7 CRISPRa kit - CRISPR gene activation of human cholinergic receptor nicotinic alpha 7 subunit |
USD 1,290.00 |
{0} Product Review(s)
Be the first one to submit a review






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China