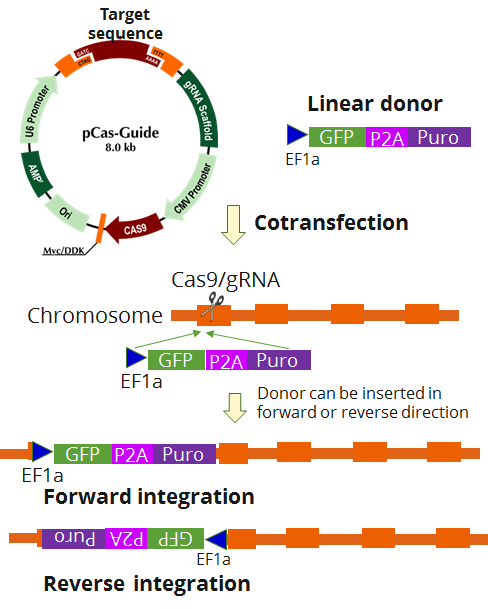
PEX5 Human Gene Knockout Kit (CRISPR)
CAT#: KN402062
PEX5 - KN2.0, Human gene knockout kit via CRISPR, non-homology mediated.
KN2.0 knockout kit validation
KN402062 is the updated version of KN202062.
USD 1,290.00
2 Weeks*
Size
Other products for "PEX5"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Format | 2 gRNA vectors, 1 linear donor |
| Donor DNA | EF1a-GFP-P2A-Puro |
| Symbol | PEX5 |
| Locus ID | 5830 |
| Disclaimer | The kit is designed based on the best knowledge of CRISPR technology. The system has been functionally validated for knocking-in the cassette downstream the native promoter. The efficiency of the knock-out varies due to the nature of the biology and the complexity of the experimental process. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NM_000319, NM_001131023, NM_001131024, NM_001131025, NM_001131026, NM_001300789, NM_001351124, NM_001351126, NM_001351127, NM_001351128, NM_001351130, NM_001351131, NM_001351132, NM_001351133, NM_001351134, NM_001351135, NM_001351136, NM_001351137, NM_001351138, NM_001351139, NM_001351140 |
| Synonyms | PBD2A; PBD2B; PTS1-BP; PTS1R; PXR1; RCDP5 |
| Summary | 'The product of this gene binds to the C-terminal PTS1-type tripeptide peroxisomal targeting signal (SKL-type) and plays an essential role in peroxisomal protein import. Peroxins (PEXs) are proteins that are essential for the assembly of functional peroxisomes. The peroxisome biogenesis disorders (PBDs) are a group of genetically heterogeneous autosomal recessive, lethal diseases characterized by multiple defects in peroxisome function. The peroxisomal biogenesis disorders are a heterogeneous group with at least 14 complementation groups and with more than 1 phenotype being observed in cases falling into particular complementation groups. Although the clinical features of PBD patients vary, cells from all PBD patients exhibit a defect in the import of one or more classes of peroxisomal matrix proteins into the organelle. Defects in this gene are a cause of neonatal adrenoleukodystrophy (NALD), a cause of Zellweger syndrome (ZWS) as well as may be a cause of infantile Refsum disease (IRD). Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008]' |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
Resources
Other Versions
| SKU | Description | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| GA103965 | PEX5 CRISPRa kit - CRISPR gene activation of human peroxisomal biogenesis factor 5 |
USD 1,290.00 |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China