Protein Kinase A regulatory subunit I alpha (PRKAR1A) (NM_212472) Human Recombinant Protein
CAT#: TP312810
Recombinant protein of human protein kinase, cAMP-dependent, regulatory, type I, alpha (tissue specific extinguisher 1) (PRKAR1A), transcript variant 3
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Species | Human |
| Expression Host | HEK293T |
| Expression cDNA Clone or AA Sequence |
Recombinant protein was produced with TrueORF clone, RC212810. Click on the TrueORF clone link to view cDNA and protein sequences.
|
| Tag | C-Myc/DDK |
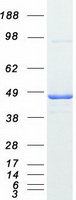
| Predicted MW | 42.8 kDa |
| Concentration | >50 ug/mL as determined by microplate BCA method |
| Purity | > 80% as determined by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining |
| Buffer | 25 mM Tris.HCl, pH 7.3, 100 mM glycine, 10% glycerol |
| Preparation | Recombinant protein was captured through anti-DDK affinity column followed by conventional chromatography steps. |
| Storage | Store at -80°C. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from the date of receipt of the product under proper storage and handling conditions. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NP_997637 |
| Locus ID | 5573 |
| UniProt ID | P10644, B2R5T5 |
| Cytogenetics | 17q24.2 |
| Refseq Size | 4356 |
| Refseq ORF | 1143 |
| Synonyms | ACRDYS1; ADOHR; CAR; CNC; CNC1; PKR1; PPNAD1; PRKAR1; TSE1 |
| Summary | 'cAMP is a signaling molecule important for a variety of cellular functions. cAMP exerts its effects by activating the cAMP-dependent protein kinase, which transduces the signal through phosphorylation of different target proteins. The inactive kinase holoenzyme is a tetramer composed of two regulatory and two catalytic subunits. cAMP causes the dissociation of the inactive holoenzyme into a dimer of regulatory subunits bound to four cAMP and two free monomeric catalytic subunits. Four different regulatory subunits and three catalytic subunits have been identified in humans. This gene encodes one of the regulatory subunits. This protein was found to be a tissue-specific extinguisher that down-regulates the expression of seven liver genes in hepatoma x fibroblast hybrids. Mutations in this gene cause Carney complex (CNC). This gene can fuse to the RET protooncogene by gene rearrangement and form the thyroid tumor-specific chimeric oncogene known as PTC2. A nonconventional nuclear localization sequence (NLS) has been found for this protein which suggests a role in DNA replication via the protein serving as a nuclear transport protein for the second subunit of the Replication Factor C (RFC40). Several alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding two different isoforms have been observed. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2013]' |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome, Transcription Factors |
| Protein Pathways | Apoptosis, Insulin signaling pathway |
Documents
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
Recombinant Protein Resources |
Other Versions
| SKU | Description | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| LC400963 | PRKAR1A HEK293T cell transient overexpression lysate (as WB positive control) |
USD 121.00 |
|
| LC403944 | PRKAR1A HEK293T cell transient overexpression lysate (as WB positive control) |
USD 121.00 |
|
| LC403945 | PRKAR1A HEK293T cell transient overexpression lysate (as WB positive control) |
USD 121.00 |
|
| LC431006 | PRKAR1A HEK293T cell transient overexpression lysate (as WB positive control) |
USD 121.00 |
|
| LY400963 | Transient overexpression lysate of protein kinase, cAMP-dependent, regulatory, type I, alpha (tissue specific extinguisher 1) (PRKAR1A), transcript variant 1 |
USD 436.00 |
|
| LY403944 | Transient overexpression lysate of protein kinase, cAMP-dependent, regulatory, type I, alpha (tissue specific extinguisher 1) (PRKAR1A), transcript variant 2 |
USD 436.00 |
|
| LY403945 | Transient overexpression lysate of protein kinase, cAMP-dependent, regulatory, type I, alpha (tissue specific extinguisher 1) (PRKAR1A), transcript variant 3 |
USD 436.00 |
|
| LY431006 | Transient overexpression lysate of protein kinase, cAMP-dependent, regulatory, type I, alpha (tissue specific extinguisher 1) (PRKAR1A), transcript variant 2 |
USD 396.00 |
|
| PH303828 | PRKAR1A MS Standard C13 and N15-labeled recombinant protein (NP_002725) |
USD 2,055.00 |
|
| PH310623 | PRKAR1A MS Standard C13 and N15-labeled recombinant protein (NP_997636) |
USD 2,055.00 |
|
| PH312810 | PRKAR1A MS Standard C13 and N15-labeled recombinant protein (NP_997637) |
USD 2,055.00 |
|
| TP303828 | Recombinant protein of human protein kinase, cAMP-dependent, regulatory, type I, alpha (tissue specific extinguisher 1) (PRKAR1A), transcript variant 1 |
USD 439.00 |
|
| TP310623 | Recombinant protein of human protein kinase, cAMP-dependent, regulatory, type I, alpha (tissue specific extinguisher 1) (PRKAR1A), transcript variant 2 |
USD 823.00 |
{0} Product Review(s)
Be the first one to submit a review






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China