SFTPB (NM_198843) Human Recombinant Protein
CAT#: TP324088
Recombinant protein of human surfactant protein B (SFTPB), transcript variant 2
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Species | Human |
| Expression Host | HEK293T |
| Expression cDNA Clone or AA Sequence |
Recombinant protein was produced with TrueORF clone, RC224088. Click on the TrueORF clone link to view cDNA and protein sequences.
|
| Tag | C-Myc/DDK |
| Predicted MW | 39.5 kDa |
| Concentration | >50 ug/mL as determined by microplate BCA method |
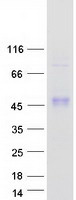
| Purity | > 80% as determined by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining |
| Buffer | 25 mM Tris.HCl, pH 7.3, 100 mM glycine, 10% glycerol |
| Preparation | Recombinant protein was captured through anti-DDK affinity column followed by conventional chromatography steps. |
| Storage | Store at -80°C. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from the date of receipt of the product under proper storage and handling conditions. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NP_942140 |
| Locus ID | 6439 |
| UniProt ID | P07988, D6W5L6 |
| Cytogenetics | 2p11.2 |
| Refseq Size | 2854 |
| Refseq ORF | 1143 |
| Synonyms | PSP-B; SFTB3; SFTP3; SMDP1; SP-B |
| Summary | 'This gene encodes the pulmonary-associated surfactant protein B (SPB), an amphipathic surfactant protein essential for lung function and homeostasis after birth. Pulmonary surfactant is a surface-active lipoprotein complex composed of 90% lipids and 10% proteins which include plasma proteins and apolipoproteins SPA, SPB, SPC and SPD. The surfactant is secreted by the alveolar cells of the lung and maintains the stability of pulmonary tissue by reducing the surface tension of fluids that coat the lung. The SPB enhances the rate of spreading and increases the stability of surfactant monolayers in vitro. Multiple mutations in this gene have been identified, which cause pulmonary surfactant metabolism dysfunction type 1, also called pulmonary alveolar proteinosis due to surfactant protein B deficiency, and are associated with fatal respiratory distress in the neonatal period. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been identified.[provided by RefSeq, Feb 2010]' |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome, Secreted Protein |
Documents
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
Recombinant Protein Resources |
Other Versions
| SKU | Description | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| LC404785 | SFTPB HEK293T cell transient overexpression lysate (as WB positive control) |
USD 121.00 |
|
| LC424653 | SFTPB HEK293T cell transient overexpression lysate (as WB positive control) |
USD 121.00 |
|
| LY404785 | Transient overexpression lysate of surfactant protein B (SFTPB), transcript variant 2 |
USD 396.00 |
|
| LY424653 | Transient overexpression lysate of surfactant protein B (SFTPB), transcript variant 1 |
USD 396.00 |
|
| PH324088 | SFTPB MS Standard C13 and N15-labeled recombinant protein (NP_942140) |
USD 2,055.00 |
{0} Product Review(s)
Be the first one to submit a review






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China