7 Important Considerations When Selecting a Protein Expression System
Aug 22, 2023
Selecting the most suitable expression system for your research depends on various factors to ensure success. Whether you're embarking on cutting-edge research or pursuing large-scale biomanufacturing, understanding the considerations involved in selecting an expression system is of utmost importance. When choosing an expression system, you should consider the following factors:?
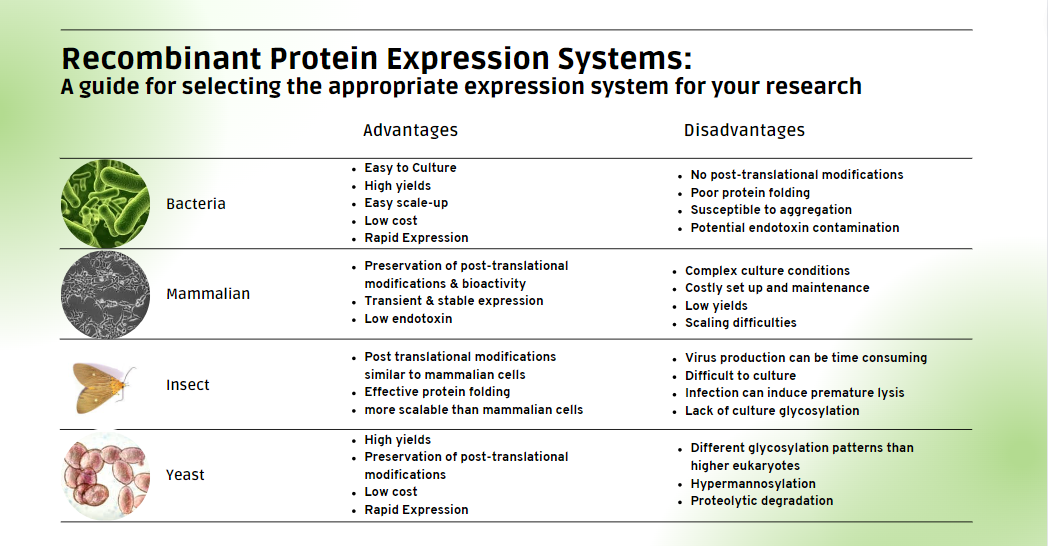
- Expression Levels: Bacterial systems offer high expression levels, making them suitable for rapid and cost-effective production of simple proteins1. Yeast and mammalian systems provide varying expression levels, with yeast offering scalability advantages and mammalian systems allowing for proper folding and post-translational modifications of complex proteins.?
- Protein Folding: Consider the system's ability to correctly fold your target protein. Bacterial systems may require co-expression of chaperones, while yeast and mammalian systems generally fold proteins correctly2.?
- Post-Translational Modifications: If your protein requires specific modifications (glycosylation, phosphorylation, etc.), mammalian and insect systems are better suited due to their ability to perform a wide range of post-translational modifications3. Yeast systems have a different glycosylation pattern than higher eukaryotes which can negatively affect protein stability, immunogenicity, and bioactivity 4,5.?
- Scalability: Evaluate the scalability of the chosen system to ensure it aligns with your production needs. Bacterial and yeast systems are often favored for their scalability, while mammalian and insect systems may have limitations1.?
- Time to Expression: Consider the time it takes for each system to achieve optimal protein expression. Bacterial systems typically offer rapid expression, while mammalian systems may require longer cultivation times.?
- Cost: Factor in the cost of media, equipment, and other resources associated with each expression system. Bacterial systems are generally economical, while mammalian and insect systems tend to be more expensive.?
Below is a table comparing the features of these expression systems. Consider the unique attributes of each system and align them with your specific needs to achieve optimal results in your recombinant protein endeavors.?
Interested in Custom Proteins?
With OriGene's custom protein service, you can now access a truly comprehensive solution tailored to your specific research needs. The flexibility offered by using insect, mammalian, or bacterial expression systems ensures that you can obtain your target protein exactly as required, be it intricate mammalian cell lines or cost-effective bacterial systems. With OriGene's renowned expertise in protein production within mammalian systems, rest assured that our established methods and processes seamlessly overcome common challenges. Let us take care of your project from start to finish. OriGene's team of experts will handle everything for you, from cDNA cloning all the way to efficient protein purification.?
Request a QuoteCitation
- Khan KH. Gene expression in Mammalian cells and its applications. Adv Pharm Bull. 2013;3(2):257-63. doi: 10.5681/apb.2013.042. Epub 2013 Aug 20. PMID: 24312845; PMCID: PMC3848218
- Rosano, Germ??n L., & Ceccarelli, E. A. (2014). Recombinant protein expression in escherichia coli: Advances and challenges. Frontiers in Microbiology, 5. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2014.00172
- Ikonomou L, Schneider YJ, Agathos SN. Insect cell culture for industrial production of recombinant proteins. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2003 Jul;62(1):1-20. doi: 10.1007/s00253-003-1223-9. Epub 2003 May 6. PMID: 12733003.
- Baghban R, Farajnia S, Rajabibazl M, Ghasemi Y, Mafi A, Hoseinpoor R, Rahbarnia L, Aria M. Yeast Expression Systems: Overview and Recent Advances. Mol Biotechnol. 2019 May;61(5):365-384. doi: 10.1007/s12033-019-00164-8. PMID: 30805909.
- Lee MH, Hsu TL, Lin JJ, Lin YJ, Kao YY, Chang JJ, Li WH. Constructing a human complex type N-linked glycosylation pathway in Kluyveromyces marxianus. PLoS One. 2020 May 29;15(5):e0233492. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0233492. PMID: 32469948; PMCID: PMC7259728.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China