RAN (N-term) Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Other products for "RAN"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
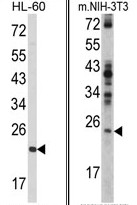
| Applications | WB |
| Recommended Dilution | ELISA: 1/1,000. Western blotting: 1/50 - 1/100. |
| Reactivities | Human, Mouse |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Immunogen | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide selected from the N-terminal region of human RAN |
| Specificity | This antibody reacts to RAN. |
| Formulation | PBS with 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide State: Liquid purified Ig |
| Concentration | lot specific |
| Purification | Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) precipitation |
| Storage | Store the antibody undiluted at 2-8°C for one month or (in aliquots) at -20°C for longer. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Stability | Shelf life: one year from despatch. |
| Gene Name | Homo sapiens RAN, member RAS oncogene family (RAN), transcript variant 1 |
| Database Link | |
| Background | RAN (ras-related nuclear protein) is a small GTP binding protein belonging to the RAS superfamily that is essential for the translocation of RNA and proteins through the nuclear pore complex. The RAN protein is also involved in control of DNA synthesis and cell cycle progression. Nuclear localization of RAN requires the presence of regulator of chromosome condensation 1 (RCC1). Mutations in RAN disrupt DNA synthesis. Because of its many functions, it is likely that RAN interacts with several other proteins. RAN regulates formation and organization of the microtubule network independently of its role in the nucleus-cytosol exchange of macromolecules. RAN could be a key signaling molecule regulating microtubule polymerization during mitosis. RCC1 generates a high local concentration of RAN-GTP around chromatin which, in turn, induces the local nucleation of microtubules. RAN is an androgen receptor (AR) coactivator that binds differentially with different lengths of polyglutamine within the androgen receptor. Polyglutamine repeat expansion in the AR is linked to Kennedy's disease (X-linked spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy). RAN coactivation of the AR diminishes with polyglutamine expansion within the AR, and this weak coactivation may lead to partial androgen insensitivity during the development of Kennedy's disease. |
| Synonyms | GTPase Ran, ARA24 |
| Reference Data | |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome, Transcription Factors |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China