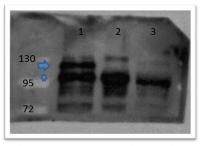
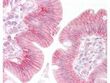
beta Catenin (CTNNB1) Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Other products for "CTNNB1"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Applications | IHC, WB |
| Recommended Dilution | ELISA: 1:25,000, WB: 1:500 |
| Reactivities | Bovine, Human, Mouse, Rat, Xenopus, Zebrafish |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Immunogen | beta catenin antibody was prepared from whole rabbit serum produced by repeated immunizations with a synthetic peptide corresponding to catenin beta-1 C-terminus. |
| Formulation | 0.02 M Potassium Phosphate, 0.15 M Sodium Chloride, pH 7.2 |
| Concentration | lot specific |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Storage | Store at -20°C as received. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from date of receipt. |
| Gene Name | catenin beta 1 |
| Database Link | |
| Synonyms | armadillo; CTNNB; MRD19 |
| Note | Beta-catenin 1 (or β-catenin 1) is a protein that is encoded by the CTNNB1 gene. β-catenin 1 is a subunit of the cadherin protein complex and has been implicated as an integral component in the Wnt signaling pathway. This pathway plays a key role in the regulation of cellular processes involved in development, differentiation, and adult tissue homeostasis. In the presence of Wnt ligand, β-catenin 1 is not ubiquitinated and accumulates in the nucleus, where it associates with T-cell factor (TCF) family members to regulate target gene expression in many developmental and adult tissues. Recruitment of b-catenin 1 to Wnt response element (WRE) chromatin converts TCFs from transcriptional repressors to activators. β-catenin 1 is also involved in the regulation of cell adhesion. It acts as a negative regulator of centrosome cohesion. Aberrant Wnt/β-catenin signaling is widely implicated in cancer, bone disorders, kidney and intestinal cell disorders and other disease states. β-catenin 1 is located in the cytoplasm when it is unstabilized or bound to CDH1. Interaction with GLIS2 and MUC1 promotes nuclear translocation. Interaction with EMD inhibits nuclear localization. The majority of β-catenin 1 is localized to the cell membrane. In interphase, colocalizes with CROCC between CEP250 puncta at the proximal end of centrioles, and this localization is dependent on CROCC and CEP250. In mitosis, when NEK2 activity increases, it localizes to centrosomes at spindle poles independent of CROCC. It further co-localizes with CDK5 in the cell-cell contacts and plasma membrane of undifferentiated and differentiated neuroblastoma cells. |
| Reference Data | |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome, ES Cell Differentiation/IPS, Transcription Factors |
| Protein Pathways | Adherens junction, Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC), Basal cell carcinoma, Colorectal cancer, Endometrial cancer, Focal adhesion, Leukocyte transendothelial migration, Melanogenesis, Pathogenic Escherichia coli infection, Pathways in cancer, Prostate cancer, Thyroid cancer, Tight junction, Wnt signaling pathway |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China