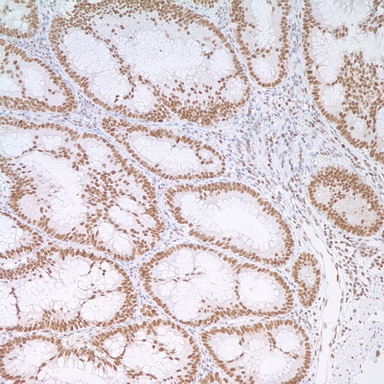
MSH2 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody [Clone ID: G219-1129]
Other products for "MSH2"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Clone Name | G219-1129 |
| Applications | IHC |
| Recommended Dilution | IHC: 1:100-1:500 |
| Reactivities | Human |
| Host | Mouse |
| Isotype | IgG1 |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Formulation | This antibody is supplied as cell culture supernatant diluted in tris buffered saline, pH 7.3-7.7, with 1% BSA and <0.1% sodium azide. |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Storage | Store at -20°C as received. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from date of receipt. |
| Gene Name | mutS homolog 2 |
| Database Link | |
| Synonyms | COCA1; FCC1; HNPCC; HNPCC1; LCFS2 |
| Note | MSH2 is a locus frequently mutated in hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer (HNPCC). When cloned, it was discovered to be a human homolog of the E. coli mismatch repair gene mutS, consistent with the characteristic alterations in microsatellite sequences (RER+ phenotype) found in HNPCC. Microsatellites are repetitive DNA sequences dispersed throughout the genome. The repetition renders them susceptible to slippage mutations. To counter this, there are families of mismatch repair (MMR) genes which correct these errors. These repair genes include MLH1, PMS2, MSH2, and MSH6. Defective MMR genes lead to accumulation of mutations in microsatellite regions, known as microsatellite instability (MSI). Colonic and endometrial carcinomas in HNPCC can be demonstrated to have MSI. MSI can also be found in 17% to 23% of non-familial endometrial carcinomas; this MSI is attributable to silencing of the MLH1 gene by promoter methylation.HNPCC is characterized by an increased risk of colon cancer and other cancers (e.g., of the endometrium, ovary, stomach, small intestine, hepatobiliary tract, upper urinary tract, brain, and skin). Individuals with HNPCC have an approximately 80% lifetime risk for colon cancer. Women with HNPCC have a 20-60% lifetime risk of endometrial cancer. Among women with HNPCC who develop both colon cancer and endometrial cancer, approximately 50% present first with endometrial cancer. 90% of patients with HNPCC have mutations of either MLH1 or MSH2. Mutations in MSH6 have been reported in approximately 7-10% of families with HNPCC. Mutations in PMS2 account for fewer than 5% of mutations in families with HNPCC.MSI testing can be demonstrated by polymerase chain reaction, molecular genetic testing, and methylation analysis of tumor tissue. However, in routine diagnostic practice, IHC is the most common clinically available method for detection of the proteins encoded by MLH1, MSH2, and MSH6. IHC is more feasible for large scale screening programs as it is more available than MSI testing. |
| Reference Data | |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome, Stem cell - Pluripotency |
| Protein Pathways | Colorectal cancer, Mismatch repair, Pathways in cancer |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China