KCNK3 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Other products for "KCNK3"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
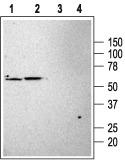
| Applications | WB |
| Recommended Dilution | WB: 1:200-1:2000; IHC: 1:100-1:3000 |
| Reactivities | Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Immunogen | Peptide (C)EDEKRDAEHRALLTRNGQ, corresponding to amino acid residues 252-269 of human K2P3.1 (TASK-1). Intracellular, C-terminal part. |
| Formulation | Lyophilized. Concentration before lyophilization ~0.8mg/ml (lot dependent, please refer to CoA along with shipment for actual concentration). Buffer before lyophilization: Phosphate buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.4, 1% BSA, 5% sucrose, 0.025% NaN3. |
| Purification | Affinity purified on immobilized antigen. |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Storage | Store at -20°C as received. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from date of receipt. |
| Gene Name | potassium two pore domain channel subfamily K member 3 |
| Database Link | |
| Background | K2P3.1 (also named TWIK-Related Acid Sensitive K+ channel, TASK-1 or KCNK3) is a member of the 2-pore (2P) domain K+ channels family that includes at least 16 members. These channels show little time or voltage dependence and are considered to be â??leakâ? or â??backgroundâ? K+ channels, thereby generating background currents which help set the membrane resting potential and cell excitation. The K2P channels have a signature topology that includes four transmembrane domains and two pore domains with intracellular N- and C termini. The functional channel is believed to be a dimer. K2P channels are regulated by diverse physical and chemical stimuli including temperature, changes in intracellular pH, mechanical stretch, inhalation anesthetics, etc. The channels can then be subclassified based in their specific activators. K2P3.1 is extremely sensitive to variations in external pH, a drop in pH from 7.7 to 6.7 will be enough to close most K2P3.1 channels. K2P3.1 channel distribution is relatively wide with high expression in the brain and heart as well as in the pancreas, kidney and lung. K2P3.1 can exist in the brain either as a homodimer or as a heterodimer with the closely related channel K2P9.1 (TASK-3). During periods of high neuronal activity a transient increase in extracellular pH has been recorded. This pH increase may stimulate K2P3.1 channel activity and hence enhance outward K+ currents. This in turn will decrease excitability in these neurons and work as a feedback mechanism. |
| Synonyms | K2p3.1; OAT1; PPH4; TASK; TASK-1; TBAK1 |
| Reference Data | |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome, Ion Channels: Potassium, Transmembrane |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China