RANTES (CCL5) Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Frequently bought together (3)
Transient overexpression lysate of chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 5 (CCL5)
USD 436.00
Other products for "RANTES"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
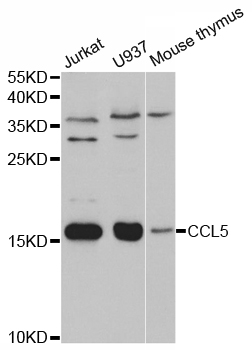
| Applications | ELISA, WB |
| Recommended Dilution | WB,1:500 - 1:2000 ELISA,Recommended starting concentration is 1 μg/mL. Please optimize the concentration based on your specific assay requirements. |
| Reactivities | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Formulation | Buffer: PBS with 0.05% proclin300,50% glycerol,pH7.3. |
| Concentration | lot specific |
| Purification | Affinity purification |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Storage | Store at -20℃. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from date of receipt. |
| Predicted Protein Size | 10kDa |
| Gene Name | C-C motif chemokine ligand 5 |
| Database Link | |
| Background | This gene is one of several chemokine genes clustered on the q-arm of chromosome 17. Chemokines form a superfamily of secreted proteins involved in immunoregulatory and inflammatory processes. The superfamily is divided into four subfamilies based on the arrangement of the N-terminal cysteine residues of the mature peptide. This chemokine, a member of the CC subfamily, functions as a chemoattractant for blood monocytes, memory T helper cells and eosinophils. It causes the release of histamine from basophils and activates eosinophils. This cytokine is one of the major HIV-suppressive factors produced by CD8+ cells. It functions as one of the natural ligands for the chemokine receptor chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 5 (CCR5), and it suppresses in vitro replication of the R5 strains of HIV-1, which use CCR5 as a coreceptor. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants that encode different isoforms. |
| Synonyms | D17S136E; eoCP; RANTES; SCYA5; SIS-delta; SISd; TCP228 |
| Reference Data | |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome, Secreted Protein, Transmembrane |
| Protein Pathways | Chemokine signaling pathway, Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction, Cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway, Epithelial cell signaling in Helicobacter pylori infection, NOD-like receptor signaling pathway, Prion diseases, Toll-like receptor signaling pathway |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China