ATF6 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody [Clone ID: 70B1413.1]
Other products for "ATF6"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Clone Name | 70B1413.1 |
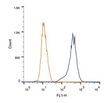
| Applications | FC, IHC, WB |
| Recommended Dilution | WB: 1-5 ug/ml, ChIP: 1:10-1:500, FC: 1 ug per million cells, IF: 1:10-1:500, IHC: 1:10-1:500, IHC-F: 1:10-1:500, IHC-P: 1:50, IP: 1:10-1:500 |
| Reactivities | Fish, Hamster, Human, Mouse, Rabbit, Rat |
| Host | Mouse |
| Isotype | IgG1, kappa |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Immunogen | This monoclonal antibody was made against a partial protein containing amino acids 1-273 of human ATF6. |
| Formulation | PBS containing 0.05% BSA, 0.05% Sodium Azide. Store at 4C short term. Aliquot and store at -20C long term. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Concentration | lot specific |
| Purification | Protein G purified |
| Storage | Store at -20°C as received. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from date of receipt. |
| Gene Name | activating transcription factor 6 |
| Database Link | |
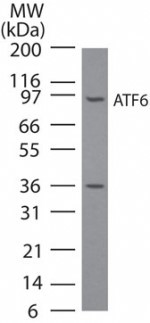
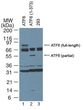
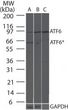
| Background | ATF6 is a constitutively expressed, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane-anchored transcription factor. ATF6 is a key transcriptional activator of the unfolded protein response (UPR), which allows mammalian cells to maintain cellular homeostasis when they are subjected to environmental and physiological stresses that target the ER (reviewed in Shen, 2005 & Prywes, 2005). The C-terminus of ATF6 is located in the ER lumen and its N-terminal DNA binding domain faces the cytosol. AFT6 plays a key role in the ER stress response by transmitting the ER stress signal across the ER membrane into the nucleus. The induction of new gene expression by ATF6 is an important aspect of the ER stress response. In response to certain stress conditions, ATF6 translocates from the ER to the Golgi. The 90 kDa full-length ATF6 is processed within the Golgi to its active 50 kDa form through sequential cleavage by site-1 and site-2 proteases (S1P and S2P). Proteolytic activation of ATF6 in the ER stress response is a mechanism to regulate membrane-bound factors, and is referred to as regulated intramembrane proteolysis. The N-terminal active ATF6 translocates to the nucleus where it binds to ER stress-response elements in ER stress-response genes (ERSRGs). ATF6 is a potent transcriptional activator of ERSRGs. The fully glycosylated form of ATF6, a 670 amino acid protein, exhibits an electrophoretic mobility of ~90 kDa in denaturing SDS-gels, in part because of the glycosylated modifications. ATF6 has 3 consensus sites for N-linked glycosylation and exists constitutively as a glycosylated protein. Differentially glycosylated ATF6 forms may result from mutations or experimental treatment. |
| Synonyms | ACHM7; ATF6A |
| Note | Chromatin Immunoprecipitation: See Donati et al, 2006 and Renna et al, 2007 for details. Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence: See Thomas et al (2005) and Kikuchi et al (2006) for details. Immunohistochemistry (frozen): See Zhu et al, 2008 for details. Immunohistochemistry (paraffin): See van Kollenburg et al (2006) for details. Immunoprecipitation: See Hong et al, 2004 for details. |
| Reference Data | |
| Protein Families | Transcription Factors |
| Protein Pathways | Alzheimer's disease |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China