Rel B (RELB) Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Frequently bought together (3)
Recombinant protein of human v-rel reticuloendotheliosis viral oncogene homolog B (RELB)
USD 823.00
Transient overexpression lysate of v-rel reticuloendotheliosis viral oncogene homolog B (RELB)
USD 396.00
Other products for "RELB"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Applications | WB |
| Recommended Dilution | WB |
| Reactivities | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Immunogen | The immunogen for anti-RELB antibody: synthetic peptide directed towards the middle region of human RELB. Synthetic peptide located within the following region: DLLPPAPPHASAVVCSGGAGAVVGETPGPEPLTLDSYQAPGPGDGGTASL |
| Formulation | Liquid. Purified antibody supplied in 1x PBS buffer with 0.09% (w/v) sodium azide and 2% sucrose. Note that this product is shipped as lyophilized powder to China customers. |
| Purification | Affinity Purified |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Storage | Store at -20°C as received. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from date of receipt. |
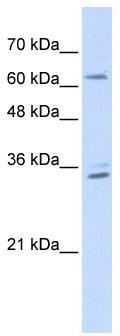
| Predicted Protein Size | 62 kDa |
| Gene Name | RELB proto-oncogene, NF-kB subunit |
| Database Link | |
| Background | NF-kappa-B is a pleiotropic transcription factor which is present in almost all cell types and is involved in many biological processed such as inflammation, immunity, differentiation, cell growth, tumorigenesis and apoptosis. NF-kappa-B is a homo- or heterodimeric complex formed by the Rel-like domain-containing proteins RELA/p65, RELB, NFKB1/p105, NFKB1/p50, REL and NFKB2/p52. The dimers bind at kappa-B sites in the DNA of their target genes and the individual dimers have distinct preferences for different kappa-B sites that they can bind with distinguishable affinity and specificity. Different dimer combinations act as transcriptional activators or repressors, respectively. NF-kappa-B is controlled by various mechanisms of post-translational modification and subcellular compartmentalization as well as by interactions with other cofactors or corepressors. NF-kappa-B complexes are held in the cytoplasm in an inactive state complexed with members of the NF-kappa-B inhibitor (I-kappa-B) family. In a conventional activation pathway, I-kappa-B is phosphorylated by I-kappa-B kinases (IKKs) in response to different activators, subsequently degraded thus liberating the active NF-kappa-B complex which translocates to the nucleus. NF-kappa-B heterodimeric RelB-p50 and RelB-p52 complexes are transcriptional activators. RELB neither associates with DNA nor with RELA/p65 or REL. Stimulates promoter activity in the presence of NFKB2/p49. |
| Synonyms | I-REL; IREL; REL-B |
| Note | Immunogen Sequence Homology: Dog: 100%; Human: 100%; Bovine: 100%; Horse: 93%; Pig: 86% |
| Reference Data | |
| Protein Families | Druggable Genome, Transcription Factors |
| Protein Pathways | MAPK signaling pathway |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China